The Grid Emission Factor (GEF) measures the carbon intensity of electricity generation in grams of CO₂ per kilowatt-hour (gCO₂/kWh). This factor considers all energy sources feeding into the grid, from fossil fuels to renewables. As the EU accelerates its green transition, understanding GEF helps evaluate which countries are leading the race toward clean energy.
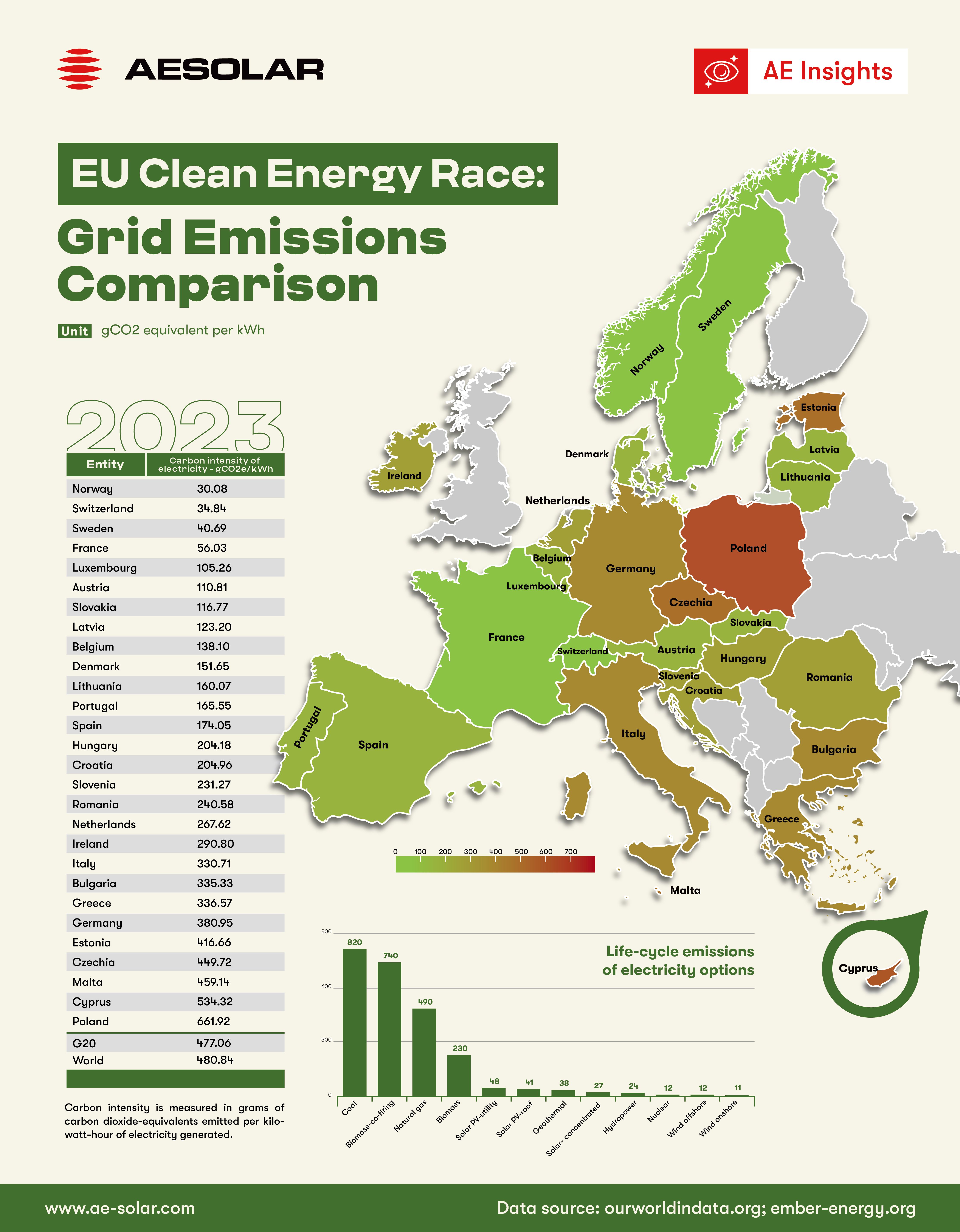
EU Grid Emissions by-Country Comparison (2023)
Data from 2023 highlights significant variations in carbon intensity across EU nations:
- Lowest emissions: Norway (30 gCO₂/kWh), Sweden (40.7 gCO₂/kWh), Switzerland (34.8 gCO₂/kWh), and France (56 gCO₂/kWh) showcase some of the cleanest electricity grids, driven by hydropower, nuclear, and wind energy.
- Highest emissions: Poland (661.9 gCO₂/kWh), Cyprus (534.3 gCO₂/kWh), and Czechia (449.7 gCO₂/kWh) still rely heavily on fossil fuels.
- Germany's grid: With 380.9 gCO₂/kWh, Germany is making strides in renewables but remains impacted by coal and gas dependency.
- EU 27 average: While specific averages vary, many EU nations are performing better than the global grid emission factor of 480.8 gCO₂/kWh.
The Role of Solar Energy in Emission Reduction
Among the renewable energy options, solar power stands out as the most scalable, cost-effective, and rapidly deployable solution. Compared to coal (820 gCO₂/kWh) and natural gas (490 gCO₂/kWh), The life-cycle emissions of rooftop solar PV are just 41 gCO₂/kWh, significantly lower than fossil fuel alternatives. This makes it one of the most effective solutions for decarbonizing power grids.
EU Policies Supporting Renewable Energy
The EU has implemented several policies to accelerate the transition to cleaner electricity:
1. European Green Deal: Aiming for climate neutrality by 2050, with renewables at the core of energy strategy.
2. REPowerEU Plan: Targets 45% renewable energy by 2030, emphasizing solar PV expansion.
3. Solar Rooftop Initiative: Mandates rooftop solar on new buildings from 2025 onwards.
4. Carbon Pricing (EU ETS): Making fossil-fuel-based power generation less competitive compared to renewables.
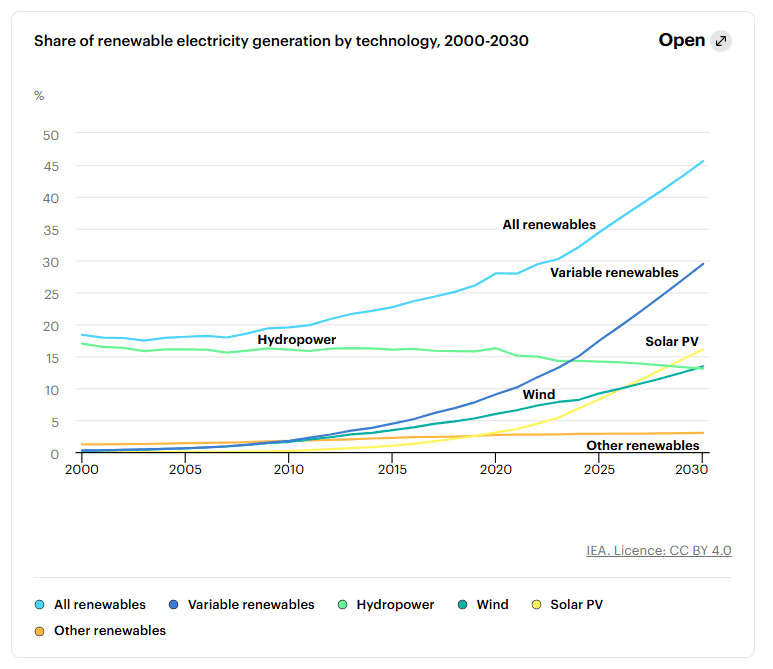
Solar Power: Fast Deployment & Cost Efficiency
Solar energy stands out as the most rapidly deployable and cost-effective renewable energy source. Unlike wind or hydropower, which require extensive site development and infrastructure, solar PV can be deployed on rooftops, carports, and open fields within months, significantly accelerating clean energy adoption. Additionally, the falling costs of solar modules, along with EU incentives, have made it one of the most accessible solutions for both businesses and households.
AESOLAR’s Commitment to a Sustainable Future
AESOLAR is actively contributing to the energy transition by providing high-efficiency solar modules that help lower grid reliance and emissions. For example, just three AESOLAR 700W solar panels installed on a rooftop in Germany can offset approximately 780 kg of CO₂ per year—a greater impact than the lifetime carbon absorption of a 30-year-old oak tree.
With governments pushing for ambitious renewable targets and businesses seeking sustainable energy solutions, solar power is poised to play a dominant role in the EU’s clean energy future.
Find AESOLAR solutions HERE