Silver, this gleaming precious metal, is not only a symbol of jewelry and currency but also a core material driving the global clean energy revolution. As the metal with the best electrical conductivity and reflectivity (reflectance up to 91%), its role in solar cells is irreplaceable—from the electrodes to the reflective layers in photovoltaic cells, silver's performance directly determines the photoelectric conversion efficiency and the reliability of the modules.
The Role of Silver in Solar Cells
Conductive Core: Silver is the core material for the front electrodes of crystalline silicon solar cells. In the metallization process of solar cells, high-temperature sintered silver paste is screen-printed to form conductive grid lines, collecting photogenerated current and reducing resistive losses. Each standard PV module consumes approximately 15-20 grams of silver, and its conductive efficiency directly impacts the module's power output.
Reflective Enhancement: Silver-coated films are used to enhance the light-capturing ability of solar panels. Research from the University of Rochester shows that adding a silver mirror to the bottom layer of perovskite solar cells can triple their conversion efficiency. Additionally, silver-based reflective films reduce light scattering losses on the cell surface, significantly improving power generation under low-light conditions.
Durability Barrier: Silver's oxidation resistance and high-temperature tolerance (melting point of 960.8°C) make it excel in module soldering and encapsulation. Compared to alternatives like conductive adhesives, silver electrodes demonstrate more stable performance in long-term outdoor aging tests, ensuring module lifespans exceeding 25 years.
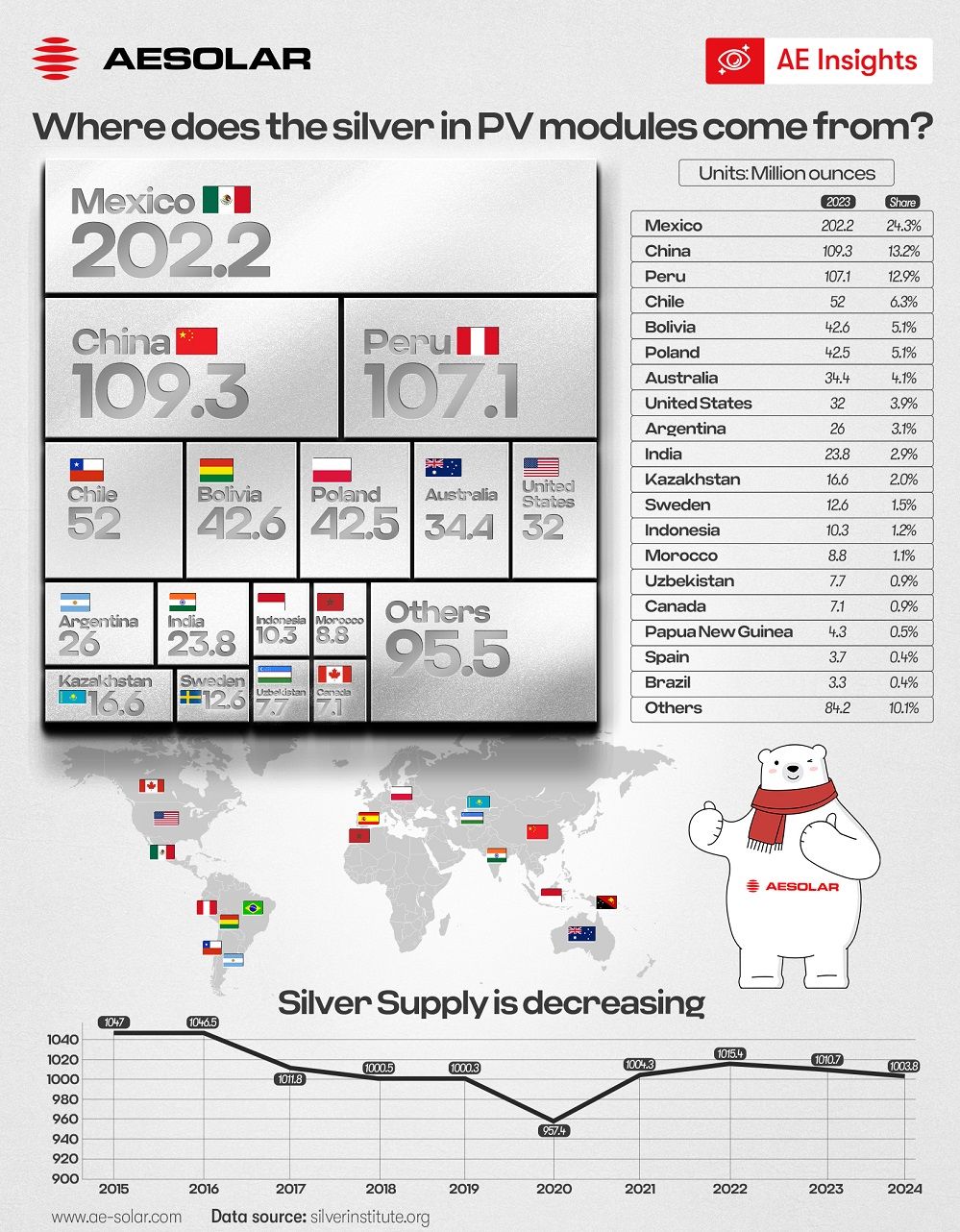
Silver Supply Chain
Global silver mining is highly concentrated in a few countries. In 2023, Mexico (24.3%), China (13.2%), and Peru (12.9%) contributed over 50% of total production, while the top ten producing countries accounted for 80%. This geographic concentration makes the supply chain highly vulnerable to policy changes or natural disasters.
Besides, the decline in silver production is concerned. From 2015 to 2024, global mine output dropped from 1,047 million ounces to 1,004 million ounces, a decrease of 4.1%. Meanwhile, the solar industry's demand is surging due to the rapid growth of PV installations—by 2030, annual demand is expected to exceed 81 million ounces, increasing silver's share of total consumption from 7.7% in 2023 to over 12%. This has led to significant price volatility, with silver prices rised by 21% in 2024.
Innovative Solutions in the Solar Industry
To mitigate these challenges, the solar industry is actively pursuing innovative solutions to reduce its reliance on silver. One promising approach is the development of 0BB (Zero Busbar) technology, which significantly reduces the amount of silver required in solar panels. By eliminating traditional busbars and optimizing the design of the conductive grid lines, 0BB technology can cut silver usage by up to 30% without compromising efficiency.
Additionally, the industry is exploring recycling initiatives to recover silver from end-of-life solar panels and electronic waste. While still in its early stages, recycling has the potential to offset a significant portion of silver demand in the coming years.
Balancing Growth and Sustainability
The solar industry’s rapid growth is a testament to its critical role in the global energy transition. However, this growth must be balanced with sustainable practices to ensure long-term viability.
Check Out Our Solar Solution