In the process of global energy transition, G20 countries, as major economies, are redefining their power sources. This shift reflects not only the differences in policy guidance, resource endowments, and technological innovation among these countries but also indicates that the global energy landscape is moving towards greater diversity and sustainability. This infographic visually illustrates the power generation of these major economies, highlighting the shift towards renewable energy while acknowledging the ongoing dominance of fossil fuels in many regions.
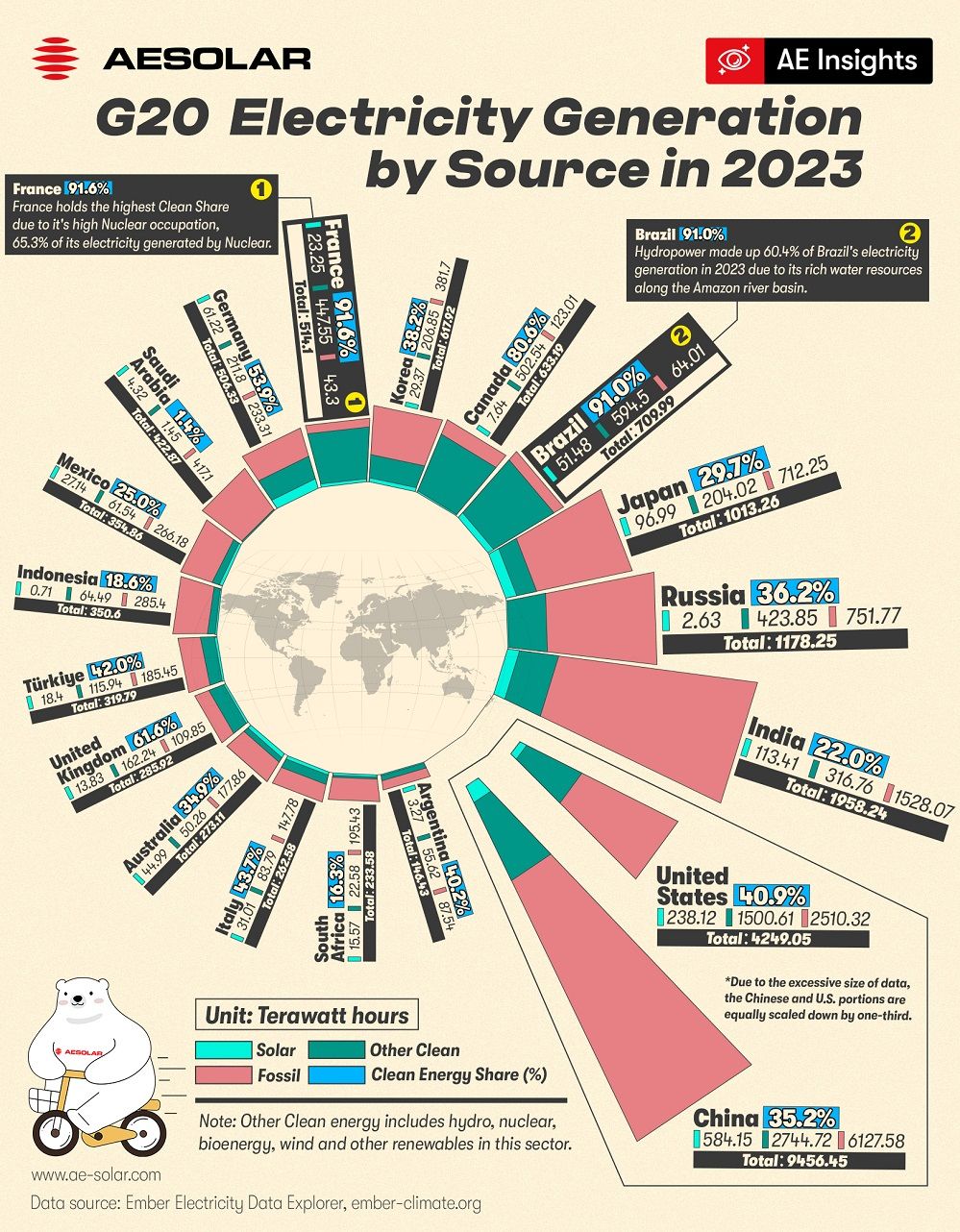
Among G20 members, the energy structures vary significantly. France and Brazil lead in the proportion of clean energy, thanks to their resource endowments and policy support. Nuclear power contributes significantly to France's electricity mix, generating 335.65 TWh, accounting for 65.3% of its total power supply, resulting in a clean energy proportion of 91.6%.
Brazil, blessed with abundant water resources, particularly in the Amazon basin, relies heavily on hydropower in its energy structure. In 2023, hydropower accounted for 60.4% of Brazil's total power generation, bringing its clean energy proportion to 91.0%. Furthermore, with the rapid development of the PV industry, Brazil’s solar power generation has reached 51.48 TWh, with an annual growth rate exceeding 120%.
In contrast, industrialized countries like China, Germany, and the United States showcase a diversified mix of clean energy. While China’s clean energy proportion is relatively modest, it leads the world in installed capacity for solar and wind energy. In 2023, China's solar power generation reached 584.15 TWh. Simultaneously, wind, nuclear, and hydropower capacities continued to expand, contributing to a total clean energy generation of 2,744.72 TWh, which, despite China’s vast power demand, represents only 35.2% of its total generation.
The United States has a more diversified clean energy structure, encompassing solar, wind, biomass, and nuclear power. In 2023, the U.S. generated 1,738.7 TWh of clean energy, accounting for 40.9% of its total power generation. Solar power contributed 238.12 TWh, with wind and nuclear energy providing 375.33 TWh and 778.16 TWh, respectively. As energy storage technology advances and grid flexibility improves, the U.S. is poised to further reduce its dependence on fossil fuels.
Germany, as a pioneer in Europe’s clean energy transition, exhibits a unique energy structure. Through policy instruments, the government has provided stable subsidies and feed-in tariff guarantees, attracting substantial investments in renewable energy. In 2023, Germany’s solar power generation reached 61.22 TWh, accounting for 12.1% of its total power generation, maintaining its position as the leader in Europe. Clean energy generation totaled 273.02 TWh, representing 53.9% of the country’s total power generation. Germany has also made significant progress in energy storage technology and smart grid construction. These measures lay the foundation for a greater integration of renewable energy into the grid, providing strong support for Germany’s energy transition.
According to the International Energy Agency’s (IEA) Electricity Market Report, by 2025, renewable energy generation will surpass coal-fired power for the first time, becoming the primary source of global power supply. This transformation is driven not only by policy initiatives but also by technological advancements and active participation from capital markets. It is expected that by 2030, global renewable energy investments will reach $4.4 trillion, with solar and wind energy becoming the main growth sectors.
As a leading global photovoltaic module manufacturer, AESOLAR continues to invest heavily in PV technology and applications, committed to providing customers with efficient and reliable clean energy solutions while continuously expanding its global presence.